Effective Strategies to Eliminate Midges Outdoors


Intro
Midges are small flying insects that can create a significant nuisance for those who enjoy outdoor spaces. Often mistaken for mosquitoes, these pests can be particularly active during warm and humid months. Their presence can detract from outdoor activities, making it crucial to understand how to control their populations effectively. In this article, we will explore various strategies to eliminate midges outdoors, from identifying these pests to applying effective treatment options. By gaining insights into prevention methods and available treatments, homeowners can create a more hospitable outdoor environment.
Pest Identification
Detailed Descriptions of Common Pests
Midges are typically small, measuring about 1 to 3 millimeters in length. They have slender bodies, long legs, and delicate wings, which distinguish them from other insects. Chironomidae is the most common family of midges, often found near water sources such as ponds and marshes. They prefer damp areas, which provide the perfect breeding ground for larvae.
Signs and Symptoms of Infestations
Identifying a midge problem early can help in managing their numbers. Look for these signs:
- Increased numbers of small flying insects, particularly around bodies of water.
- Bites resembling mosquito bites, which may cause irritation.
- Swarms that become evident in the evening or at dusk.
If you notice these symptoms in your outdoor space, it may indicate an infestation that requires immediate attention.
Prevention Strategies
Home Maintenance Tips for Pest Prevention
To minimize midge populations, regular home maintenance should be a priority. Here are some effective tips:
- Eliminate Standing Water: Regularly check for and remove any standing water around your property, such as in buckets, birdbaths, and clogged gutters.
- Trim Vegetation: Keep shrubs and grasses well-trimmed. Overgrown areas provide shelter for midges.
- Improve Drainage: Ensure that your yard has proper drainage to discourage midge breeding.
Natural Deterrents and Barriers
Several natural methods can act as effective deterrents against midges. Consider implementing these strategies:
- Essential Oils: Oils like citronella and eucalyptus can repel midges. Create homemade sprays using these oils for application.
- Garlic Repellent: Mixing garlic with water can create a natural repellent. Spray it around your outdoor space for a mild deterrent.
- Fans: Installing outdoor fans can help create airflow, making it harder for midges to swarm and settle.
Treatment Options
Overview of Chemical vs. Natural Treatments
When dealing with a significant midge problem, both chemical and natural treatment methods can be effective. Chemical treatments, such as insecticides, can eliminate midges quickly, but they may have environmental impacts. On the other hand, natural treatments tend to be safer for plants, pets, and people but may require more frequent applications.
Step-by-Step Guides for DIY Treatments
For those looking to take a hands-on approach, follow these guides for DIY treatments:
Chemical Treatment:
- Choose an insecticide labeled for midge control.
- Apply the product according to the manufacturer’s directions.
- Focus applications near breeding sites like water bodies or damp soil.
Natural Treatment:
- Mix equal parts of water and essential oil (like citronella).
- Pour the mixture into a spray bottle.
- Spray around your home and yard, paying special attention to areas where midges gather.
Understanding Midges
Understanding midges is crucial for anyone looking to manage these small, often irritating pests effectively. These insects can disrupt outdoor activities and impact the comfort of homes and landscapes. By grasping the nature of midges—what they are, their life cycle, and common species—individuals can make informed decisions on how to control their population. This knowledge enables proactive measures, reducing the likelihood of infestations before they become severe.
Defining Midges
Midges are small, flying insects belonging to the family Chironomidae. These pests are distinguished by their slender bodies and long legs. While they may resemble mosquitoes, midges are typically smaller and lack the characteristic biting behavior of their more notorious relatives. Instead of feeding on blood, midges primarily consume nectar. Their presence, however, can still be a nuisance, particularly in large numbers.
Life Cycle of Midges
The life cycle of midges is significant in understanding how to control their populations. Midges undergo a complete metamorphosis, consisting of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The female midges lay their eggs in aquatic environments, such as ponds or marshes. After hatching, the larvae develop in the water, feeding on organic matter. As they mature, they transition into pupae before finally emerging as adults. This cycle can occur rapidly under favorable conditions, making it essential to address midge habitats effectively.
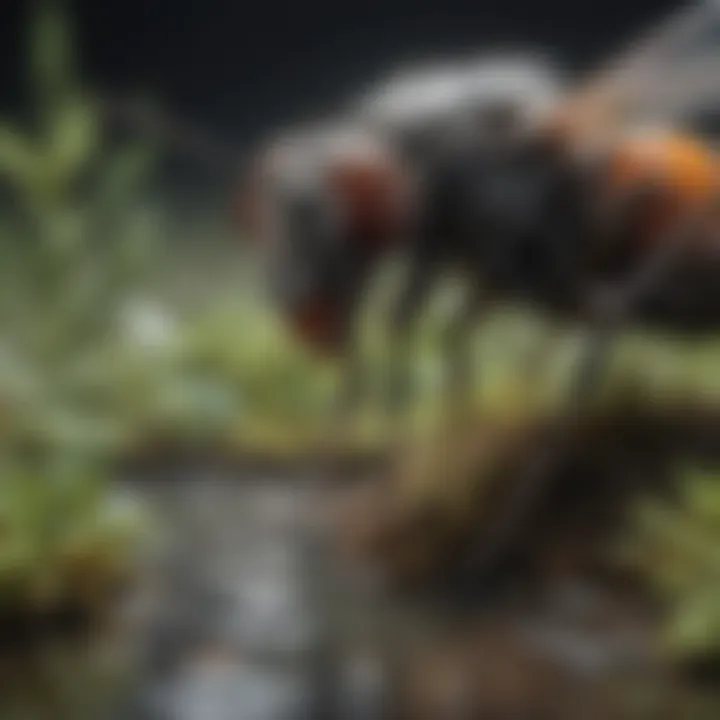


Common Species of Midges
There are several common species of midges. The most prevalent include species like the Culicoides and Chironomus.
- Biting Midges (Culicoides): Known for their painful bites, these midges are often found in coastal areas or near still water.
- Non-Biting Midges (Chironomus): These are more commonly encountered and do not cause any discomfort, yet their swarming behavior can still be bothersome.
Understanding these species helps in identifying the specific type of midge problems one might face and informs the strategies that can be employed for effective management.
Identifying Midge Infestations
Identifying midge infestations is a crucial step in effectively managing these pests outdoors. Understanding how to spot midge activity not only helps in recognizing an issue early but also assists in implementing targeted control measures. Midges are small and often overlooked, which makes early detection essential. Their presence can indicate a larger issue, potentially leading to more severe infestations if not addressed promptly. This section explores key signs of midge activity, their preferred habitats, and how to distinguish them from similar pests.
Signs of Midge Activity
To effectively combat midges, homeowners should familiarize themselves with the signs of their activity. Common indicators include:
- Swarming Behavior: Midges are known for their swarming tendencies, especially during twilight and dawn. Observing groups of small flying insects hovering around people or outdoor lights is typically a strong sign of midge presence.
- Bites and Irritation: Many individuals experience bites or skin irritation after exposure to midges. This can manifest as itchy welts on exposed skin.
- Presence of Midge Larvae: Check for midge larvae in stagnant water sources like ponds, bird baths, or flower pots. The larvae are small and often found in clusters near the water’s surface.
Recognizing these signs can help you determine not just the presence of midges but also the level of control required.
Locations of Midge Habitats
Midges are attracted to specific environments that facilitate their life cycle. Identifying these habitats is vital in preventing infestations. Common locations for midge breeding include:
- Stagnant Water Sources: Midges thrive in still or slow-moving water. Areas like marshes, ponds, and ditches provide ideal breeding conditions for midge larvae.
- Vegetation Near Water: The presence of dense vegetation along waterways is another attraction point. Plants provide shelter for adult midges and a conducive environment for the larvae.
- Urban Areas with Water Features: Water fountains, bird baths, and poorly maintained pools in residential areas serve as perfect habitats for midge reproduction.
Regular inspections of these areas can help homeowners identify potential breeding sites and take preventative measures before a significant infestation occurs.
Differentiating Midges from Other Pests
Midges can be mistaken for other small flying insects, such as mosquitoes or certain flies. Distinguishing midges from these pests is important to implement appropriate control strategies. Here are some distinguishing features:
- Physical Appearance: Midges are generally smaller than mosquitoes, with a more slender body. They have long legs and are often seen in clouds or swarms.
- Feeding Behavior: Unlike mosquitoes, which bite and feed on blood, midges primarily feed on nectar and are less aggressive. Adult midges do not typically bite unless they feel threatened; this is a key differentiation point.
- Time of Activity: Midges are most active during twilight and dawn, while mosquitoes can be active at any time, including night. Observing the time of day can help identify which pest is present.
Being knowledgeable about these differences can help homeowners choose the correct management techniques, leading to more effective control of midge populations.
Preventative Measures
Preventative measures are crucial in managing midge populations. By focusing on elimination before an infestation occurs, homeowners can significantly reduce the chances of these pests becoming a nuisance. Preventative actions help in maintaining both the comfort and health of outdoor spaces, making them more enjoyable for family and friends. They are also environmentally responsible, minimizing the need for more aggressive treatments later.
Eliminating Breeding Grounds
One of the primary steps in preventing midge infestations is eliminating their breeding grounds. Midges thrive in wet environments, especially in stagnant water. Homeowners should regularly inspect their property for potential water sources. Here are key actions to consider:
- Remove standing water from bird baths, clogged gutters, or any containers that can hold rainwater.
- Fill in any depressions in yards that tend to collect water.
- Ensure that swimming pools are properly maintained and covered when not in use.
By proactively addressing areas where midges might breed, you effectively reduce their population right from the source.
Environmental Adjustments
Making simple environmental adjustments can also deter midges from settling in your outdoor spaces. Here are some suggested changes:
- Proper landscaping: Use plants that are less attractive to midges. Bluebell and marigold plants can be beneficial.
- Introduce aeration: If water features are part of the landscape, consider adding aeration devices. Moving water is less hospitable to midges.
- Optimize lighting: Bright lights can attract various insects, including midges. Using yellow or sodium vapor lights reduces attraction. Keep lights positioned away from outdoor seating areas.
These adjustments, while minor, can create an environment less conducive to midge presence.
Maintaining Outdoor Spaces
Regular upkeep of outdoor spaces is essential to control midge populations. Taking care of lawns, gardens, and patios not only promotes a healthy environment but also acts as a deterrent to pests.
- Lawn care: Keep grass trimmed and lawns adequately watered. Overly moist and unkempt areas attract midges.
- Cleaning routines: Regularly clear away organic debris such as leaves and grass clippings that can hold moisture.
- Mulching: Use dry mulch instead of wet ones to keep the ground drier in garden beds.
In summary, effective maintenance practices support the goal of reducing midge populations while ensuring that outdoor spaces remain enjoyable for all.

Chemical Control Options
Chemical control options are critical in managing midge populations effectively. When traditional methods do not yield desired results, these approaches can offer targeted solutions. Chemical treatments possess the capability to rapidly reduce midge numbers. However, they come with responsibilities. It is essential to choose the right compounds and apply them correctly. This is to ensure efficacy while minimizing harm to non-target species and the environment.
Insecticides for Midge Control
Insecticides are the most commonly used chemical options for controlling midges. These chemicals work by disrupting the biological processes of midges, leading to their death. Common insecticides for midge control include Pyrethroids and Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti). Pyrethroids are synthetic chemicals that mimic natural pyrethrins, found in chrysanthemum flowers. They are effective against adult midges. Bti, on the other hand, is a naturally occurring bacterium that targets midge larvae specifically.
Choosing the right insecticide is vital. Here is a short list of factors to consider:
- Specific targets — adult vs. larvae
- Application timing — needs to correspond with life cycles
- Resistance — rotating different classes of insecticides
Application Methods
The application method significantly affects the effectiveness of insecticides. They can be applied using several methods, including:
- Spraying: Most common for treating large areas. Ensure even coverage for thorough results.
- Granules: These are spread around breeding sites. They dissolve in water and target larvae.
- Fogging: Quick dispersal for immediate results, especially in open areas.
Timing is crucial. It is often best to apply treatments during peak midge activity, which usually occurs in the evenings or at dawn. Proper equipment and calibration of spray devices are also important to ensure maximum efficiency and minimal waste.
Safety Precautions
Safety precautions cannot be overlooked when applying chemical control methods.
- Protective Gear: Always wear gloves, masks, and goggles to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Applicator Training: Ensure that individuals applying the insecticides are properly trained and familiar with the product.
- Read Labels: Product labels contain vital information about safe usage and potential hazards.
- Monitor Weather Conditions: Rain or high winds can affect treatment efficacy and safety.
Always consider non-chemical options alongside chemicals for a more sustainable approach to midge control.
Natural Treatment Solutions
Natural treatment solutions play a significant role in effectively managing midge populations without compromising environmental integrity. These approaches are often preferred by those seeking alternatives to chemical interventions. By utilizing natural remedies, homeowners and pest control professionals can ensure safety for humans, pets, and beneficial wildlife. Natural options tend to be less toxic and promote a sustainable environment, making them a viable choice in midge control strategies.
Essential Oils and Repellents
Essential oils are frequently cited for their repellent properties against various insect species, including midges. Oils such as citronella, eucalyptus, and lavender can act as natural deterrents. They contain compounds that midge find unpleasant, thus reducing their presence in a given area. Homeowners can create their own natural repellent by mixing essential oils with a carrier oil or water and spraying it onto exposed skin or around outdoor living spaces.
"Natural repellents offer a peaceful, eco-friendly alternative to harmful pesticides, keeping your space serene and safe from midges."
Natural Larvicides
When addressing midge control, targeting the larval stage is crucial. Natural larvicides can be employed to disrupt the life cycle of these pests. A product like Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) is effective, as it is a bacterium that targets midge larvae specifically. Applying Bti to stagnant water sources where midges breed can drastically reduce their populations, ensuring fewer adult midges emerge to disrupt outdoor activities.
Natural larvicides often require care in application to avoid harming beneficial insects. It is important to follow guidelines specific to the product to maximize effectiveness while maintaining ecological balance.
Utilizing Predatory Insects
Introducing predatory insects can serve as a natural control method for managing midge populations. Species such as dragonflies and damselflies prey on midge larvae. By creating a habitat conducive to these predators, such as adding a small pond or planting native vegetation, homeowners can enhance natural predation. This will help reduce midge populations over time without additional interventions.
Incorporating these predatory species into your garden can foster a more diverse and healthy ecosystem, simultaneously offering a long-term solution to midge infestations.
Technological Solutions
In addressing the challenges posed by midges in outdoor environments, technological solutions play a pivotal role. These innovations offer efficient, targeted, and often environmentally friendly ways to manage and control midge populations. Homeowners and pest control professionals increasingly recognize the importance of employing technology in their strategies. By integrating technological solutions, it is possible to reduce reliance on chemical treatments, thereby promoting a more sustainable approach to pest management.
Ultrasonic Pest Repellents
Ultrasonic pest repellents are devices that emit sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, specifically designed to impact insect behavior. These devices aim to create an environment that is uncomfortable for midges, encouraging them to vacate the area without causing harm. The usage of ultrasonic repellers offers several benefits:
- Non-toxic: There is no chemical pesticide involved, making them safe for children and pets.
- Ease of use: Simply plug the device into an outlet or use batteries, and let it work continuously.
- Coverage: Many devices claim to cover a considerable area, making them useful for larger outdoor spaces.
However, it is important to consider that effectiveness can vary. Research on their efficacy against midges, specifically, is limited. They may work better for some types of insects than others.
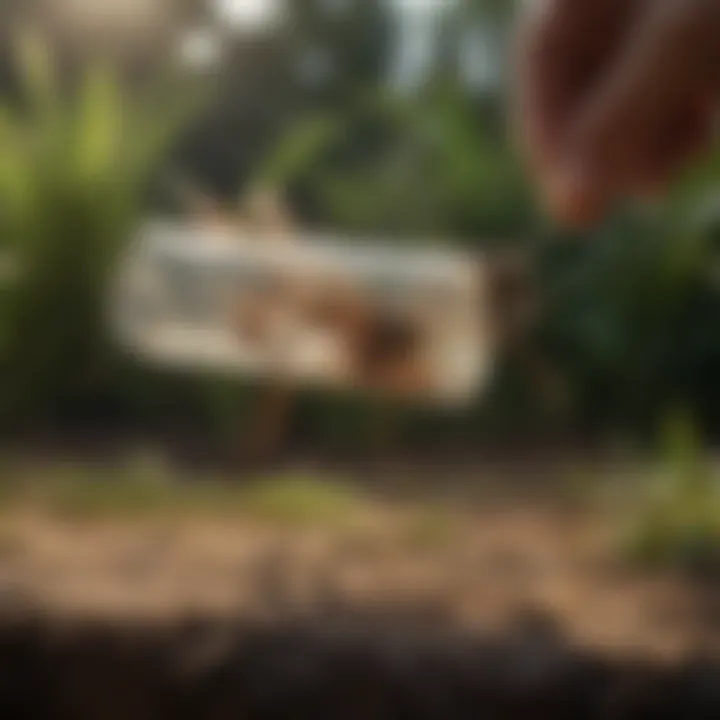


Midge Traps
Midge traps are a practical approach to controlling midge populations. These traps utilize a variety of mechanisms to attract and capture the pest, effectively reducing their numbers in specific areas. Here are some of the notable types of traps available:
- Chemical attractants: Some traps use scents or pheromones to lure midges in.
- Light traps: These traps use light to attract midges, making them more likely to enter and become ensnared.
- Sticky traps: Some traps rely on adhesive surfaces that capture midges upon contact.
The primary benefits of midge traps include:
- Low maintenance: Once set up, these traps require minimal oversight.
- Targeted control: They specifically target midges, reducing impacts on non-target species.
An important consideration is the positioning of these traps. They should be placed near known midge habitats to maximize effectiveness.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Smart monitoring systems are gaining traction in the realm of pest control. These systems use technology to provide real-time data on pest activity, including midges. By employing sensors and connectivity features, homeowners can receive alerts about midge presence or behavior.
Key features of smart monitoring systems include:
- Data Collection: Continuous monitoring allows for better understanding of when and where midge populations surge.
- Remote Access: Many systems send alerts directly to a smartphone or computer, facilitating instant response.
- Optimized Management: With accurate data, homeowners can tailor their pest control efforts more effectively.
Ultimately, investing in smart monitoring creates a proactive approach to pest management, ensuring sustained control of midge populations while reducing unnecessary chemical use.
Effective technological solutions not only enhance pest management strategies but also align with sustainable practices, ensuring a healthier outdoor environment for all.
By embracing these technological advancements, homeowners can navigate the ongoing battle against midges more successfully. The interplay of various tools, from ultrasonic repellers to smart monitoring systems, allows for a multi-faceted approach that can significantly mitigate the discomfort caused by these pests.
Post-Control Measures
Post-control measures are essential steps following the implementation of midge control strategies. They ensure the effectiveness of the measures taken and contribute to long-term management of midge populations. By evaluating the success of control efforts and adjusting strategies as needed, homeowners can prevent future infestations. These measures also allow for responsible management practices that minimize the impact on surrounding ecosystems.
Evaluating Control Effectiveness
Evaluating control effectiveness involves assessing how well the chosen methods have reduced midge populations. This analysis should be thorough and systematic. Here are key components to consider:
- Monitoring Midge Activity: Regularly check for the presence of midges in outdoor spaces. Notice any small clouds of flying midges near vegetation or standing water.
- Assessing Impact on Environment: Observe if the control methods have affected beneficial insects or surrounding wildlife. Ensure that the environment remains balanced and functional.
- Feedback from Users: Gather insights from family members or guests about their experiences outdoors. Their feedback can highlight areas needing further attention.
"Continuous evaluation is crucial for successful pest management. Adjusting techniques based on observed outcomes can lead to more effective strategies."
Long-term Midge Management Strategies
To maintain a midge-free environment, long-term management strategies must be established. These strategies focus on minimizing conditions favorable for midge survival and reproduction. Consider these practices:
- Routine Landscape Maintenance: Regularly trim vegetation and clear debris that can serve as breeding sites.
- Water Management: Reduce standing water by filling in puddles or using drainage solutions to eliminate stagnant areas.
- Community Awareness: Share knowledge with neighbors about midge management. Collective efforts can lead to better control in broader areas.
Establishing these strategies fosters resilience against future infestations and supports a healthier outdoor environment.
Environmental Considerations
When implementing post-control measures, environmental considerations are paramount. Acting responsibly is key to ensuring that midge control does not disrupt local ecosystems. Important factors to consider include:
- Impact on Non-target Species: Evaluate whether control methods harm beneficial insects and animals. Aim to select strategies that target midges specifically without causing wider ecological harm.
- Chemical Residue Monitoring: If using chemical solutions, monitor their residual effects on soil and water. Make necessary adjustments to safeguard the environment.
- Adoption of Eco-friendly Practices: Whenever possible, prefer natural solutions and sustainable practices. This approach not only helps in managing midges but also protects the local flora and fauna.
Finale
Recap of Effective Strategies
A review of the methods discussed reveals a range of effective strategies. Here are key takeaways that encapsulate the best practices for midge control:
- Prevention is Key: Preventative measures such as removing standing water and managing vegetation play a significant role in minimizing breeding sites.
- Chemical Control: Utilizing insecticides can provide immediate relief, yet it is important to choose products that are eco-friendly and effective against midges specifically.
- Natural Solutions: Incorporating natural remedies, including essential oils and the introduction of predatory insects, offers sustainable alternatives for long-term management of midge populations.
- Technological Aids: The use of midge traps and monitoring systems enhances the ability to control and assess midge activity effectively.
- Evaluation and Adaptation: Reassessing control measures routinely ensures that strategies remain effective and environmental considerations are respected.
Encouraging Responsible Management Practices
It is critical for homeowners to adopt responsible management practices in their efforts to control midges. Such practices ensure not only the efficacy of the strategies employed but also protect the surrounding ecosystem. Here are some important elements to consider:
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the life cycle and habits of midges. Knowledge empowers better decision-making.
- Sustainable Choices: Opt for methods that have minimal impact on non-target species. Chemical treatments should always be the last resort.
- Community Involvement: Engage with neighbors to share resources and knowledge. Collective efforts can significantly enhance control measures on a larger scale.
- Long-term Focus: Shift the mindset from immediate fixes to long-term management of the environment. Create outdoor spaces that deter midges naturally.
"Understanding and respect for the environment ensures that our efforts in controlling pests like midges lead to sustainable outdoor enjoyment."
Implementing responsible practices not only addresses the current midge issue but also helps maintain a harmonious coexistence with nature.

